Table of Contents
- Cytochrome P450
- Interactions with CYP Participation in Intestines
- Cytochrome CYP3A4
- Bioaccessibility and Drug Interactions
- Drug Interaction with Participation of CYP3A4
- Drug Interactions with Statins Participation
- Drug Interactions with Participation of Antihypertensive Agents
There are many inhibitors of CYP3A4 which is one of the most important cytochromes in human organism. Around 60% of oxidized medications coming in organism with food are bio-transformed with participation of this enzyme system.
Cytochrome P450
 Cytochrome P450 is a big group of enzymes responsible for metabolism of xenogenic organic compounds and medical drugs. Enzymes of cytochrome P450 group perform oxidizing biological transformation of medical drugs and a number of other endogenous bioorganic substances and thus fulfilling detoxication function. Metabolism of many classes of medicines happens with participation of cytochromes.
Cytochrome P450 is a big group of enzymes responsible for metabolism of xenogenic organic compounds and medical drugs. Enzymes of cytochrome P450 group perform oxidizing biological transformation of medical drugs and a number of other endogenous bioorganic substances and thus fulfilling detoxication function. Metabolism of many classes of medicines happens with participation of cytochromes.
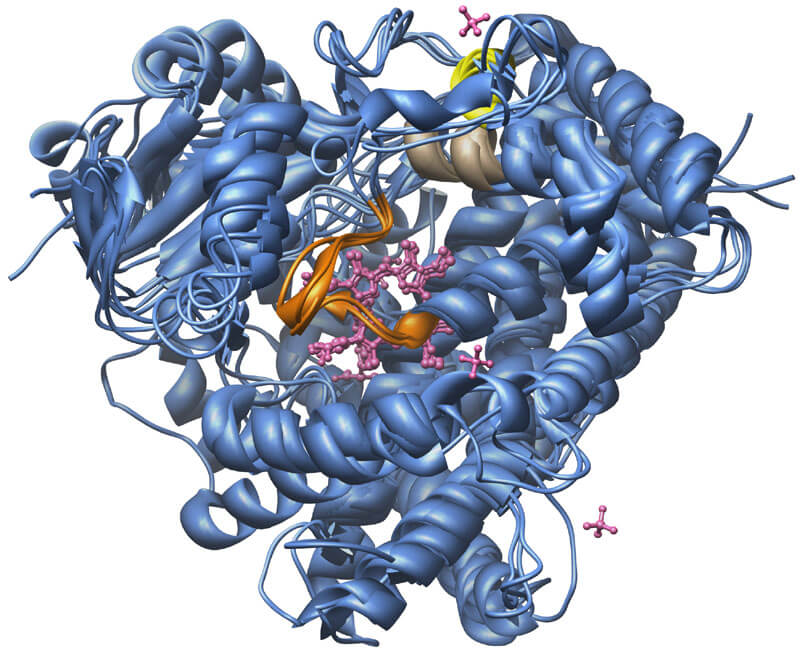
Cytochrome P450 is a complex of protein with covalently attached heme (metalloprotein) providing connection of oxygen. Heme is a complex of protoporphyrin IX and bivalent ferrum atom. Number 450 means that restored heme connected with CO differs from maximum of light absorption at the wavelength 450 nanometer (nm).
Cytochromes P450 participate in not only metabolism of medications, but also in transformation of hemoglobin into bilirubin, steroids synthesis, etc. All isoforms of cytochrome P450 are united in groups CYP1, CYP2, CYP3. There subgroups inside each group are named A, B, C, E. Within the subgroups isoforms are marked by index numbers. For instance, CYP2C19 is a name of 19th cytochrome in a row of subgroup C, group 2. There are around 250 various kinds of cytochrome P450 and among them 50 are located in human organism and only 6 of them (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4) relate to metabolism of medicines.
Cytochrome P450 activity is influenced by many factors: smoking, alcohol, age, genetics, diet, diseases. These factors are responsible for development of individual characteristics of enzymes P450 work and for determination of medical interaction effects of a specific patient.
Besides, it should be mentioned that not all cytochrome groups are equally affected by inductors and inhibitors action. It is well known that there are many inhibitors of CYP3A4, whereas CYP2D6 is considered to be non-inducible. CYP3A4 is one of the most important cytochromes in human organism. Around 60% of oxidized medications are bio-transformed with participation of this enzyme system. CYP3A4 is localized in apical part of enterocytes of narrow intestine and hepatocytes. Bio-transformation of medicines and other substances coming in organism with food is performed by this cytochrome before the drug gets into blood circulation and performs its action. This effect got its name from pre-system metabolism or metabolism of the first passage. The typical example of the drug with pre-system metabolism is calcium-channel blocker, felodipine. It is absorbed completely from gastro-intestinal tract and is exposed to pre-system metabolism in enterocytes and hepatocytes with participation of cytochrome P450. But only 15% of the drug gets in blood circulation and causes this effect.
Interactions with CYP Participation in Intestines
Inhibition of CYP activity in intestines may cause changes in pre-system metabolism. Isoenzyme CYP3A4 prevails in CYP system in human intestinal tract. Its activity level is considered to be an important factor determining degree of medicines bioaccessibility. Many drugs, such as cyclosporine, midazolam, nifedipine after peroral intake undergo per-system metabolism in intestinal wall. Thus, inhibition of CYP3A4 in intestines plays a key role in interactions with participation of these drugs.
Particular clinical consequences of CYP3A4 competitive inhibition in intestines depend on relative affinity to this enzyme of both medicines which are taken simultaneously. Metabolism of the medicines with low affinity to CYP3A4 in intestinal wall (for example, felodipine or simvastatin) decreases and causes enhancement of their peroral bioaccessibility by several times. At the same time, substances with higher affinity to CYP3A4 than proton pump inhibitors, such as ketoconazole and clarithromycin may inhibit metabolism of proton pump inhibitors and other drugs and increase content of the latter ones in blood plasma accordingly. These changes of bioaccessibility of the drugs taken simultaneously may modify their efficiency and frequency of side-effects development, although this effect was not examined by clinical trials.
 Cytochrome CYP3A4
Cytochrome CYP3A4
Enzyme CYP3A4 catalyzes sulfoxidation causing formation of sulfonate group. CYP3A4 is one of the most important cytochromes of pharmaceutics, since it is used to bio-transform around 60% of oxidable medicines. Although CYP3A4 activity is widely varied, it is not exposed to pleomorphism.
Location of CYP3A4 is apical membranes of narrow intestine erythrocytes and hepatocytes relieves medicines’ metabolism occurring before getting of substances in blood circulation. Genetic defect of CYP3A4 may cause development of secondary QT prolongation syndrome after the intake of cisapridum and as a consequence of cardiac arrhythmia.
CYP3A4 is a principle enzyme in metabolism of the following medicines:
- immunologic depressants (ciclosporin, sirolimus, tacrolimus);
- medicines taken during chemotherapy (anastrozol, cyclophosphamide, docetaxel, erlotinib, tyrphostin, etoposide, holoxane, paclitaxel, tamoxifen, tenyposide, vinblastine, vindesine, gefitinib);
- antifungal agents (clotrimazole, ketoconazole, itraconasole);
- macrolides (clarithromycin, erythromycin);
- tricyclic antidepressants (amitriptyline, clomipramine, imipramine);
- antidepressant medications – selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (escitalopram, citalopram, fluoxetine, sertraline);
- antipsychotic drugs (aripiprazole, haloperidol, ziprasidone, risperidone);
- opioids (alfentanil, codein, methadone, fentanyl);
- benzodiazines (alprazolam, clonazepam, midazolam, flunitrazepam);
- hypolipidemic statins (atorvastatin, lovastatin, simvastatin);
- calcium-channel blockers (amlodipine, verapamil, diltiazem, nifedipine, felodipine);
- reproductive hormones (levonorgestrel, mifepristone, testosterone, estradiol, ethinylestradiol, finasteride);
- also, amiodarone, buspirone, venlafaxine, sildenafil, etc.
CYP3A4 also participates (but is not a main enzyme) in metabolism of PPI (omeprazole, esomeprazole), cisapride, etc.
Inhibitors of CYP3A4:
- HIV protease inhibitors (indinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir);
- Antibiotics- macrolides (clarithromycin, telithromycin, erythromycin);
- Grapefruit juice components (bergamottin);
- antifungal agents (clotrimazole, ketoconazole, fluconazole, aprepitant, quercetine, nefazodone);
- H-blocker cimetidine;
- Analgetic buprenorphine;
- Coffee component
CYP3A4 inductors:
- antiepileptic agents and mood stabilizing agents (carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin);
- tutsan component, hyperforin;
- also, modafinil, nevirapine, rifampicin, phenobarbital, etravirine, efavirenz and many others.
Bioaccessibility and Drug Interactions
Bioaccessibility is a percent of active substance (percent of the total dosage) reaching system blood circulation in unchanged form and providing medicines effect. For felodipine the bioaccessibility after peroral intake is around 15%.
It is worth mentioning that if a medicine has low bioaccessibility after peroral intake due to high pre-system metabolism, it means that the accompanying purpose of medicines or other substances influencing pre-system metabolism (which are its inductors and inhibitors) may change its bioaccessibility considerably as well as its action and side-effects. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 cytochrome may improve bioaccessibility of medicine, increase its concentration in blood and thus enhance the effect which is compared with acute overdose.
And on the contrary, a medication with high bioaccessibility during peroral intake will be less exposed to risk of similar interaction, since its concentration in blood in regular terms is near to maximal. Nevertheless, even such medicines may have medical interactions, for example as a result of decrease of hepatic elimination from organism due to long-term parallel appropriation of CYP3A4 inhibitor. Intravenous assignment of medicine providing 100% bioaccessibility may solve this issue.
Drug Interaction with Participation of CYP3A4
Zymolytes:
- bioaccessibility <10% (lovastatin, simvastatin);
- bioaccessibility 30-70% (amiodarone, carbamazepine, diazepam, losartan, diltiazem, nifedipine, sildenafil);
- bioaccessibility >70% (amlodipine, dexamethasone, quinidine)
Inductors: carbamazepine, dexamethasone, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampicin.
Inhibitors: amiodarone, clarithromycin, cyclosporine, erythromycin, HIV protease inhibitors, ketoconazole.
One of the most dangerous consequences of undesired drug interaction may be in the form of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia known as torsade de pointes. This type of ventricular arrhythmia is more frequently met in conditions of QT interval elongation.
Development of polycardia was registered on the top of several medicines which caused their blockage on the market. They include widely used antihistaminics causing no hypnotic action, terfenadine, astemizole, as well as gastro-intestinal promotility agents, cisapride. These medicines caused dose-dependent relationship of potassium flow blockage in heart conductive path cells resulting in deferred ventricular depolarization of ECG-phenomenon of QT interval elongation. As a result, the risk of severe rhythm disturbance increased.
It should be mentioned that all blocked medicines have their safe alternative – antihistaminics, such as cetirizine, fexofenadine (active metabolite of terfenadine) and loratadine, causing no hypnotic action either. Cisapride’s place was taken by metoclopramide and domperidone causing no QT interval elongation.
Other undesirable effects occurring as a result of drug interactions are enhanced due to direct or side-effects of medicines (hypotension and ankle edema resulting from increase of bioaccessibility of felodipine, diffusive myodynia because of decrease of pre-system metabolism of statins).
Drug Interactions with Statins Participation
While gaining popularity, statins are characterized by low or very low indicators of bioaccessibility (less than 10% - lovastatin and simvastatin, 10-30% - atorvastatin and fluvastatin). The increase of bioaccessibility of lovastatin, simvastatin and atorvastatin on the top of CYP3A4 inhibitors may result in diffusive myodynia, increase of creatine phosphokinase level, severe degeneration of sceletal muscles (rhabdomyolysis) and severe renal impairment.
10-20-fold concentration increase of lovastatin and simvastatin in blood because of drug interaction of the medicines with CYP3A4 inhibitors is registered. The level of atorvastatin having a higher bioaccessibility enhances to a lesser degree – 2-4-fold. In comparison with the afore-mentioned medicines, pravastatin is minimally metabolized by CYP3A4; serious interactions with its participation are unlikely. Fluvastatin is metabolized by CYP2C9 and may become an alternative for patients taking CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Drug Interactions with Participation of Antihypertensive Agents
Hypotension is a widely spread dose-dependent side-effect of antihypertensive agents. Some of them (felodipine, nifedipine, amlodipine, diltiazem, losartan) are zymolytes of CYP3A4 cytochrome. The most significant of them are calcium channel-blocking agents. There are a lot of cases of serious undesirable drug interactions with participation of dihydropyridines with low bioaccessibility (felodipine, nifedipine). Relatively safe alternative for these medicines among patients taking CYP3A4 inhibitors may become amlodipine with high bioaccessibility if taken orally.
For instance, macrolide antibiotic, azithromycin doesn’t affect CYP3A4 activeness and may be used as an alternative to clarithromycin and erythromycin. Antifungal agent, fluconazole is a good substitution of CYP3A4 inhibitors, ketoconazole and itraconasole.
My Canadian Pharmacy Pro Team with Johnathan Blazer MD - www.mycanadianpharmacypro.com