What is Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy?
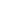
 Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy, to put it simply, is a condition when the man’s prostate gland is enlarged. As this gland is enveloping the man’s first part of the urethra, the hypertrophy can lead to a series of complications, mostly associated with problems with urinating.
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy, to put it simply, is a condition when the man’s prostate gland is enlarged. As this gland is enveloping the man’s first part of the urethra, the hypertrophy can lead to a series of complications, mostly associated with problems with urinating.
This is because the prostate gland is responsible for producing a fluid that is expelled into the urethra to further mix with spermatozoa during the ejaculation process.
This milky fluid works as both a lubricant and nutrition for the sperms.
Getting back to Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy, which is also known as Benign Prostatic hypertrophy, or, simply, enlarged prostate. It is the condition characterized by the size of the prostate gland increased as compared to the normal size. Why is it called benign? Because it is not cancer, and it does not increase the risk of cancer.
When the prostate due to its gradual enlargement reaches the certain size, its tissues may start compressing the urethra. This compression can lead to the blockage of the urine flow and as a consequence can become a cause of various problems connected with urination. In addition, it may cause urinary tract infection.
How common is Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy among males?
When a man reaches 50 years of age, he is having a 75 percent chance of having an enlarged prostate. As a man ages, it gets even worse as far as these risks are concerned.
What are the main known causes of Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy?
There are six main problems that can cause prostate complications:
» Hormonal imbalances
Men’s organisms produce more testosterone than estrogen up until their 30s. At around age 35, hormonal inversion occurs, and men start producing more estrogen than testosterone. By the time the man hits the age of 60, he makes twice as much estrogen vs testosterone.
Some of this testosterone turns into dihydrotestosterone, because of the enzyme 5α-reductases, also known as 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenases, which converts good testosterone into a bad one. Why is it bad? Because this DHT is the main cause of hair loss and prostate enlargement.
» Cancer
One of the types of estrogen converted from testosterone is responsible for many changes in the male’s body. In short, it makes the body of a man more feminine. The second thing it does, it causes prostate cancer. In the United States, prostate cancer is the most common type of cancer across non-skin cancer. It is also the second leading cause of cancer among men in the US.
» Zinc deficiency
Individual organs in our bodies have a specific elements requirements. And, when they do not get what they need, they may malfunction. A zinc deficiency can lead to BHP because for the prostate gland, zinc is a required element. zinc also can become harder to absorb when we age, which leads to wide spread zinc deficiencies we see today. We recommend trying various pumpkin extracts, which are high in zinc.
» Cadmium toxicity
Cadmium toxicity is related to the cause of zinc deficiency in the sense that the latter usually leads to the former. Cadmium is a metal commonly found in soft drinks, cigarette smoke, and some other places. Cadmium can cause fatigue, hair loss, high blood pressure, arthritis, impotence, and prostate complications. All the “good” elements are having their counterparts in “bad” elements due to their similar molecular structure. As cadmium is similar in chemical structure to zinc, our bodies can take it as zinc, absorbing it and poisoning it. Over the time, absorbed cadmium accumulates in the prostate gland and can cause problems. If a man would take supplemental zinc for his whole life, it would add some protection against cadmium absorption.
» Calcification
Calcium is crucial in keeping our bones and teeth healthy. What is less known about calcium is that when we age, calcium starts to move from bones and teeth where it belongs into the soft tissues. When calcium does this, it turns from the beneficial mineral into the pathological one. For example, when calcium moves into the kidneys, we get kidney stones. When calcium migrates into the arteries, we get arteriosclerosis. And, when calcium moves into the prostate, we get prostatic calculi, also known as prostate stones.
Prostate, in addition to being a gland, works as a small pump, and like any pump it must be free of debris in order to function properly. As we age, these small prostate stones accumulate, reducing prostate’s functionality.
» Infection
In addition to cancer, the prostate is susceptible to viral and parasitic infections.
To battle these we need Ellagic acid, which works as antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral and antiparasitic as well.
Ellagic acid inhibits the viral enzyme gyrase, which is only found in bacteria. Without this enzyme bacteria cannot coil, it unspools and then dies.
Unlike traditional antibiotics targeting only specific bacteria, ellagic acid works efficiently on all bacteria.
What are the common treatments for BPH?
The treatments of BPH are divided into the two large classes of medications, which differ in their function.
These are:
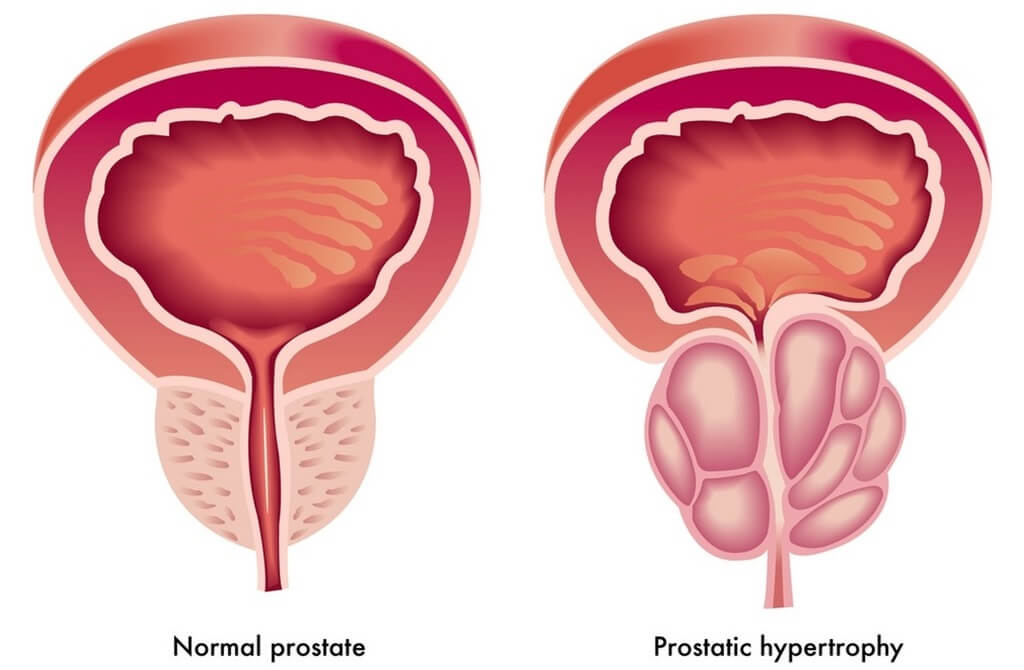
- Alpha-blockers. These medications relax the smooth muscle in the prostate as well as in the bladder neck, this way relieving the blockage of the urine flow.
- 5α-reductases inhibitors. These medications inhibit the production of dihydrotestosterone, the hormone we were talking about, which is responsible for prostate cancer.
Each group has a different mechanism of action and, therefore, it is crucial to understand the nature of your particular problem. We recommend you not to purchase any of these medications without consulting a medical specialist. The professional team of urologists of Canada Pharmacy is available for discussing your particular situation.
Alpha-blockers that are available at Canada Pharmacy include:
1.Targeting the urinary tract:
- alfuzosin (Uroxatral);
- silodosin (Rapaflo);
- tamsulosin (Flomax, generic).
2. Targeting the urinary tract but also affecting several other tissues across the body. For that reason, these are called non-selective agents.
- doxazosin (Cardura, generic),
- terazosin (Hytrin, generic).
What are differences between the mechanism of action of Alpha-blockers and 5α-reductases inhibitors?
 As the prostate gland gets enlarged, it squeezes the urethra. It leads to disruption of the urinary tract. To complicate the matters, the prostate gland may bolster up to the bladder. If that is the case, the overall amount of urine the bladder can keep reduces.
As the prostate gland gets enlarged, it squeezes the urethra. It leads to disruption of the urinary tract. To complicate the matters, the prostate gland may bolster up to the bladder. If that is the case, the overall amount of urine the bladder can keep reduces.- The blockers affect several receptors situated in the walls of the muscles of the prostate gland. When y0ou block alpha-1 receptors, the muscles cannot contract anymore, instead they remain relaxed, which leads to a normal flow of urine.
- The inhibitors, on the other hand, prevent 5–alpha reductase, which is the enzyme responsible for converting hormone testosterone into hormone dihydrotestosterone, the latter prompting the prostate to grow. As the result of this blockage, the prostate has to shrink.
Which of these medications doctors at Canada Pharmacy would recommend for its patients?
When a patient consults us at Canada Pharmacy mycanadianpharmacypro.com asking which group of medications would work best for him, we generally follow common guidelines for all urologists.
When it comes to the blockers, they are good for getting rid of problems associated with urination. They are also helping immensely in making urination less frequent. In general, they are good for men with their prostate glands of a smaller size.
On the other hand, the inhibitors are designed to treat larger prostate glands. When drugs from the first group do not work, it is time to consider this class as it has a better reputation for minimizing the chance that a man would be recommended to treat his disease with a help of surgery, or would be prone to have further complications such as acute urinary retention.
It is also should be noted, that these two groups are not counter-indicative of each other. The medications sometimes work best in combination.
Is the combination therapy possible?
The studies have shown that the drugs of both groups taken in combination return better results, indeed.
Those who combined these two reduced the risk of further complications with their prostate glands by 65 percent as compared with placebo. These numbers are way higher than when a medication of each of the group was taken alone.
Studies have also shown that the combination therapy is working best for men with their prostate glands of 25 grams of weight, or more.
Usually, when these two groups are taken in combination, after a certain period of time. It is not necessary taking the “quicker” of the two types of medications anymore, and the patients get their pills restricted to only one group.
You should consult one of the urologists in our team regarding which is the best way for the treat your BPH. We will also calculate for you the costs of each type of a treatment.
What if a patient is not responsive to these medications?
- There are patients that are non-responsive to either class of the medication. There are several non-invasive methods which can help dealing with the problem.
- These non-surgical treatments utilize heat to cause cell death, also known as necrosis in prostate tissue.
- The heat is being delivered in the small amount and targets a specific location in the tissue in order to minimize the risk of the unwanted damage.
- There are many procedures, and each clinic is specializing in the heat treatment may have its own method. Mainly these methods differ in the type of energy used.
- Transurethral resection of the prostate is a surgical procedure for removal of prostate tissue through the urethra. This procedure has been around for a long time and is considerate the ultimate procedure for the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy.
- Today, in the United States and Canada at least, it is usually performed only when medications we described above as well as less invasive treatments do not work.
What a patient with Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy can do at home before he buys BPH drugs online?
We recommend you to apply several lifestyle strategies that can help both in dealing with Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy.
All of these require performance on a daily basis for achieving belter results:
- One trick you can apply is reducing the amount of all fluids you consume when there is soon to be a situation during which going to a bathroom to urinate might be uncomfortable. The simple example is before going to bed. Another common example is before going to a place where a restroom might be hard to find or is out of reach, like during a sports game.
- Another advice in regards to drinks is to get rid of the drinks that belong to diuretics. Diuretics is a common term for a liquid substance that promotes the process known as diuresis, which is essentialy the bigger production of urine. Such drinks would include:
- Alcohol (you know that when drinking beer one is forced to go to a bathroom way too often, but actually any alcohol is prompting bigger urine production.
- Any beverages that contain caffeine. These include coffee, tea (black, green, and some sorts of herbal), all sorts of colas and various types of lemonades in particular.
- Another method we recommend is using a double-voiding technique, applied whenever you urinate. After you’ve finished urinating, just wait a couple of seconds more and make sure no urine comes out. When you do it each time, it ensures that the bladder is totally void of urine.
- The set of exercises to enhance the performance of your bladder. Consider two of these.
When you feel the urge to urinate, hold awhile before you can’t really stop it. It will make the tissues and the muscles of your bladder more trained; they are trained and get stronger like any other muscles in our bodies.
For those of the patients with Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy who takes any other medications, it would be useful to ascertain that these medications do not a prompt release of more urine or anyhow affect the muscles in the bladder.
Such medications include:
- Diuretics, for example, lots of medications that are designed to treat high blood pressure. They promote the urination.
- Antispasmodic medications.
- Some of the anti-allergic pills
- Some of the neurotransmitter-inducing medications. These are too many and they are different, but, for example, those of this class that is prescribed to treat Parkinson’s disease and various disorders that have symptoms of depression, are often making the bladder releasing more urine than usual.
Of course, it is recommended to consult your doctor, whether this would be your urologist or just a regular physician, to find out which of the medications you use make your prostate complications even worse.